Science
Researchers Enhance Biofuel Supply Chain Resilience Amid Disruptions
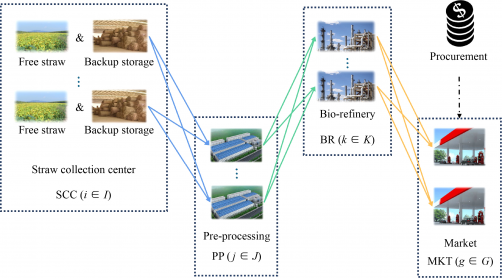
Researchers at Tianjin University have unveiled a novel approach to enhancing the resilience of biofuel supply chains. Their study, titled “Optimization Design Method for Biofuel Resilient Supply Chain Considering Node Disruption Impacts in a Two-Stage Stochastic Programming Framework,” was published in Frontiers of Chemical Science & Engineering, Volume 19, Issue 6. This research addresses a critical challenge faced by businesses as economic globalization intensifies, resulting in increasingly complex and large-scale supply chain systems.
As companies navigate rising uncertainties and the heightened risk of disruptions, the need for resilient biofuel supply chains becomes paramount. The study highlights the urgent requirement for supply chains to withstand potential disruptions while ensuring security and competitiveness. Traditional supply chain design methods have struggled to effectively quantify and evaluate disruption risks, limiting their ability to mitigate these challenges.
To tackle this issue, the researchers introduced an improved Node Disruption Impact Index, featuring adjustable parameters that reflect cost changes arising from disruptions at various nodes. This innovative index aids in identifying nodes with different risk levels, allowing businesses to evaluate the potential impact of disruptions more effectively. The adjustable parameters can be tailored to suit the specific needs of supply chain enterprises, enabling a strategic balance between economic benefits and supply chain resilience.
Application of the Two-Stage Stochastic Programming Model
In their research, the team applied the newly developed index to assess the fluctuation range of node uncertainties. They created a two-stage stochastic programming supply chain optimization model that incorporates a mechanism to address potential high disruption risks. This model was tested on a biofuel supply chain case study in Guangdong Province, demonstrating its practical applicability.
The results of the case study revealed that the proposed model significantly outperformed traditional models when high-risk nodes experienced interruptions. Specifically, it showed improved performance in terms of both cost efficiency and market delivery rates. This finding underscores the effectiveness of the proposed method in enhancing the design of resilient supply chains, thereby providing valuable insights for businesses operating within the biofuel sector.
The full research paper can be accessed for further details at: https://journal.hep.com.cn/fcse/EN/10.1007/s11705-025-2548-z.
-

 Science3 months ago
Science3 months agoUniversity of Hawaiʻi Joins $25.6M AI Project to Monitor Disasters
-

 Business3 months ago
Business3 months agoForeign Inflows into Japan Stocks Surge to ¥1.34 Trillion
-

 Entertainment2 months ago
Entertainment2 months agoHudson Williams Gains Popularity as Breakout Star on Heated Rivalry
-

 World3 months ago
World3 months agoBoeing’s Merger with McDonnell Douglas: A Strategic Move Explained
-

 Science2 months ago
Science2 months ago$1.25M Grant Advances Hawaiʻi’s Real-Time Hazard Monitoring
-

 Entertainment3 months ago
Entertainment3 months agoSydney Sweeney Embraces Body Positivity Amid Hollywood Challenges
-

 Top Stories3 months ago
Top Stories3 months agoBOYNEXTDOOR’s Jaehyun Faces Backlash Amid BTS-TWICE Controversy
-

 Top Stories3 months ago
Top Stories3 months agoUrgent Farewell: Joleen Chaney Leaves Legacy at KFOR
-

 World3 months ago
World3 months agoFrench Film Explores Group Therapy in ‘Group – The Schopenhauer Project’
-

 Top Stories3 months ago
Top Stories3 months agoMarc Buoniconti’s Legacy: 40 Years Later, Lives Transformed
-

 Lifestyle4 months ago
Lifestyle4 months agoKelsea Ballerini Launches ‘Burn the Baggage’ Candle with Ranger Station
-

 Top Stories3 months ago
Top Stories3 months agoCarson Wentz Out for Season After Shoulder Surgery: Urgent Update









