Science
Researchers Develop Biodegradable Implants for Body Monitoring
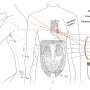
A team of researchers has unveiled a groundbreaking soft, biodegradable wireless sensing device capable of monitoring multiple internal signals from the human body over long distances. This innovative technology, developed by a group led by Prof. Su Yewang from the Institute of Mechanics of the Chinese Academy of Sciences, along with Dr. Li Shuang from Tsinghua University and Prof. Yu Xinge from City University of Hong Kong, was detailed in a study published in the journal Nature.
The newly created implant is designed to function effectively at distances of up to 16 centimeters, ensuring accurate readings despite varying body positions and angles. This capability marks a significant advancement in medical technology, offering a potential solution for continuous health monitoring without the need for invasive procedures.
Enhancing Internal Body Monitoring
The development addresses a growing need for non-invasive monitoring systems that can provide real-time data on various bodily functions. Traditional methods often require bulky equipment or invasive procedures, which can be uncomfortable for patients. In contrast, this biodegradable device offers a more patient-friendly alternative, reducing both discomfort and risk.
The implants are constructed from soft materials that can easily integrate with the human body, minimizing the foreign body response typically associated with traditional sensors. By being biodegradable, these devices also present an eco-friendly option, aligning with global efforts to reduce medical waste.
Researchers emphasized that the device’s wireless capabilities and precision make it suitable for a range of applications, from monitoring vital signs to tracking the effectiveness of treatments. The technology could play a crucial role in personalized medicine, allowing healthcare providers to tailor interventions based on real-time data.
Future Implications and Applications
The implications of this technology extend beyond patient comfort. The ability to monitor internal signals from a distance could revolutionize how healthcare providers approach diagnostics and treatment. Continuous monitoring could lead to earlier detection of complications and more timely interventions, ultimately improving patient outcomes.
As the research team prepares for the next stages of development, they are also exploring potential collaborations with medical institutions. This could facilitate clinical trials and pave the way for real-world applications of the technology.
The study represents a significant leap forward in the field of biomedical engineering, showcasing the potential to merge technological innovation with healthcare needs. As researchers continue to refine the device, the future of internal body monitoring looks promising, with the potential to enhance both patient care and the sustainability of medical practices.
-

 Science3 months ago
Science3 months agoUniversity of Hawaiʻi Joins $25.6M AI Project to Monitor Disasters
-

 Business3 months ago
Business3 months agoForeign Inflows into Japan Stocks Surge to ¥1.34 Trillion
-

 Entertainment2 months ago
Entertainment2 months agoHudson Williams Gains Popularity as Breakout Star on Heated Rivalry
-

 World3 months ago
World3 months agoBoeing’s Merger with McDonnell Douglas: A Strategic Move Explained
-

 Science2 months ago
Science2 months ago$1.25M Grant Advances Hawaiʻi’s Real-Time Hazard Monitoring
-

 Entertainment3 months ago
Entertainment3 months agoSydney Sweeney Embraces Body Positivity Amid Hollywood Challenges
-

 Top Stories3 months ago
Top Stories3 months agoBOYNEXTDOOR’s Jaehyun Faces Backlash Amid BTS-TWICE Controversy
-

 World3 months ago
World3 months agoFrench Film Explores Group Therapy in ‘Group – The Schopenhauer Project’
-

 Top Stories3 months ago
Top Stories3 months agoUrgent Farewell: Joleen Chaney Leaves Legacy at KFOR
-

 Top Stories3 months ago
Top Stories3 months agoMarc Buoniconti’s Legacy: 40 Years Later, Lives Transformed
-

 Lifestyle4 months ago
Lifestyle4 months agoKelsea Ballerini Launches ‘Burn the Baggage’ Candle with Ranger Station
-

 Top Stories3 months ago
Top Stories3 months agoCarson Wentz Out for Season After Shoulder Surgery: Urgent Update









