Science
Harvard Breakthrough Uncovers Silica’s Role in Flat Optics
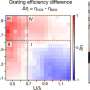
A recent discovery at Harvard University has unveiled the significant potential of silica in the field of optical metasurfaces. These ultra-thin, flat structures are designed to manipulate light at the nanoscale, demonstrating capabilities that could surpass traditional optical devices such as lenses and mirrors. The findings could lead to advancements in various applications, from telecommunications to consumer electronics.
Research teams at Harvard focused on the unique properties of silica, a material often overlooked in optics. Their investigation revealed that silica can effectively control light in innovative ways, prompting a reevaluation of materials previously considered unsuitable for advanced optical technologies. This breakthrough opens doors for developing more efficient and compact optical systems.
Silica’s Unique Properties and Implications
The research highlights silica’s ability to enable high-performance optical metasurfaces, which are essential for the next generation of optical devices. Unlike conventional optics that rely on bulky components, these metasurfaces are lightweight and can be manufactured at a lower cost, potentially transforming sectors reliant on optical technology.
According to the lead researcher, Dr. Emily Chen, the findings suggest that silica’s performance can be optimized for specific applications. “Our work demonstrates that silica is not just a standard material but can be tailored to create high-efficiency optical components,” she stated. This adaptability could significantly impact industries such as augmented reality and advanced imaging systems.
The research team conducted extensive experiments to validate their findings, testing various configurations of silica-based metasurfaces. They found that these structures could manipulate light in ways previously thought possible only with more complex materials. The implications for consumer electronics and telecommunications are profound, as these advancements could lead to smaller, more powerful devices that maintain high optical quality.
Future Applications and Industry Impact
The potential applications of silica-based optical metasurfaces are vast. Industries ranging from healthcare to aerospace could benefit from the enhanced performance and reduced size of optical components. For instance, in medical imaging, more compact systems could lead to better diagnostic tools that are easier to use in clinical settings.
The research aligns with ongoing trends in materials science that prioritize sustainability and efficiency. As industries seek to reduce costs and environmental impact, the use of silica—a widely available and non-toxic material—could become increasingly appealing.
In conclusion, the unexpected discovery at Harvard University highlights a significant shift in the understanding of materials used in optics. With silica’s newfound potential, researchers anticipate a wave of innovations that could redefine how we interact with light in everyday technology. As the field progresses, further studies will likely explore the practical implementation of these findings, shaping the future of optical devices around the globe.
-

 Science3 months ago
Science3 months agoUniversity of Hawaiʻi Joins $25.6M AI Project to Monitor Disasters
-

 Business3 months ago
Business3 months agoForeign Inflows into Japan Stocks Surge to ¥1.34 Trillion
-

 Entertainment2 months ago
Entertainment2 months agoHudson Williams Gains Popularity as Breakout Star on Heated Rivalry
-

 World3 months ago
World3 months agoBoeing’s Merger with McDonnell Douglas: A Strategic Move Explained
-

 Science2 months ago
Science2 months ago$1.25M Grant Advances Hawaiʻi’s Real-Time Hazard Monitoring
-

 Entertainment3 months ago
Entertainment3 months agoSydney Sweeney Embraces Body Positivity Amid Hollywood Challenges
-

 Top Stories3 months ago
Top Stories3 months agoBOYNEXTDOOR’s Jaehyun Faces Backlash Amid BTS-TWICE Controversy
-

 World3 months ago
World3 months agoFrench Film Explores Group Therapy in ‘Group – The Schopenhauer Project’
-

 Top Stories3 months ago
Top Stories3 months agoUrgent Farewell: Joleen Chaney Leaves Legacy at KFOR
-

 Top Stories3 months ago
Top Stories3 months agoMarc Buoniconti’s Legacy: 40 Years Later, Lives Transformed
-

 Lifestyle4 months ago
Lifestyle4 months agoKelsea Ballerini Launches ‘Burn the Baggage’ Candle with Ranger Station
-

 Top Stories3 months ago
Top Stories3 months agoCarson Wentz Out for Season After Shoulder Surgery: Urgent Update









