Science
Astronomers Discover Forming Rings Around Centaur Chiron
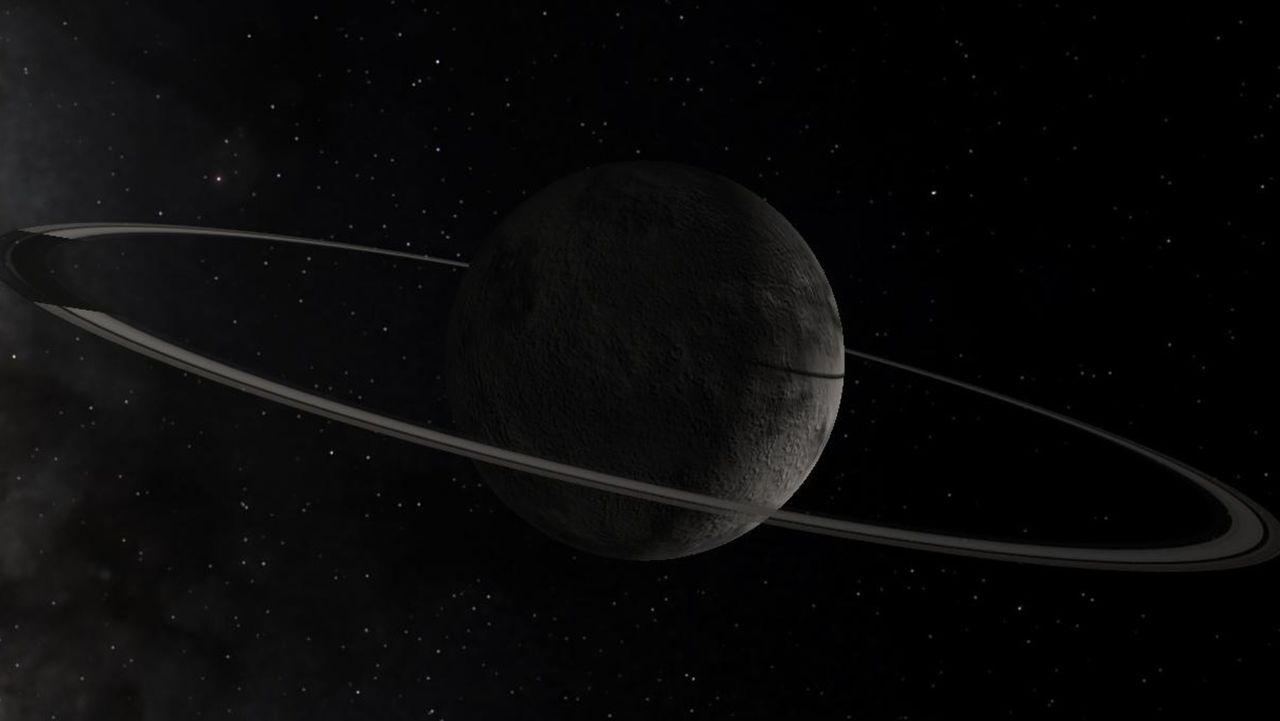

Astronomers have made a groundbreaking discovery by observing the formation of a ring system around the centaur 2060 Chiron, marking the first time such a phenomenon has been documented. This finding, derived from data collected at Brazil’s Pico dos Dias Observatory in 2023, reveals that Chiron is encircled by four distinct rings along with additional diffuse material.
Understanding Chiron and its Unique Rings
First identified in 1977, Chiron is classified as a centaur, a type of celestial object found between the orbits of Jupiter and Neptune. These bodies exhibit characteristics of both comets and asteroids. Chiron, which orbits the Sun between Saturn and Uranus, has a diameter of approximately 200 kilometers (about 125 miles) and is composed of rock, water ice, and organic compounds.
The recently discovered rings appear to consist of water ice and rocky material, potentially originating from a collision between Chiron and another celestial body. The rings are located at varying distances from Chiron’s center: approximately 273 kilometers (about 170 miles), 325 kilometers (about 202 miles), 438 kilometers (about 272 miles), and 1,400 kilometers (about 870 miles). Researchers have noted that the outermost ring may not possess the stability required to be classified as a permanent feature, necessitating further observations.
Implications of the Discovery
What makes Chiron’s ring system particularly fascinating is its ongoing development. This observation of an evolving ring system is unprecedented, providing valuable insights into the processes governing the formation of rings and satellites around smaller celestial bodies. By comparing the latest observations with data from previous years, specifically from 2022, 2018, and 2011, researchers observed rapid changes in the ring structure.
“It is an evolving system that will help us understand the dynamical mechanisms governing the creation of rings and satellites around small bodies, with potential implications for various types of disk dynamics in the universe,” said Braga Ribas, an astronomer at the Federal University of Technology-Parana and co-author of the study.
The findings have been documented in a study published in the Astrophysical Journal Letters on October 14, 2025. This discovery not only expands our understanding of ring systems beyond the well-known examples of Saturn, Uranus, Neptune, and Jupiter but also sheds light on the dynamic processes that shape these intriguing celestial formations.
As astronomers continue to monitor Chiron and its evolving rings, this research could provide essential clues about the broader mechanisms at play in the universe, potentially informing future studies of similar celestial bodies.
-

 Science3 months ago
Science3 months agoUniversity of Hawaiʻi Joins $25.6M AI Project to Monitor Disasters
-

 Business3 months ago
Business3 months agoForeign Inflows into Japan Stocks Surge to ¥1.34 Trillion
-

 Entertainment2 months ago
Entertainment2 months agoHudson Williams Gains Popularity as Breakout Star on Heated Rivalry
-

 World3 months ago
World3 months agoBoeing’s Merger with McDonnell Douglas: A Strategic Move Explained
-

 Science2 months ago
Science2 months ago$1.25M Grant Advances Hawaiʻi’s Real-Time Hazard Monitoring
-

 Entertainment3 months ago
Entertainment3 months agoSydney Sweeney Embraces Body Positivity Amid Hollywood Challenges
-

 Top Stories3 months ago
Top Stories3 months agoBOYNEXTDOOR’s Jaehyun Faces Backlash Amid BTS-TWICE Controversy
-

 World3 months ago
World3 months agoFrench Film Explores Group Therapy in ‘Group – The Schopenhauer Project’
-

 Top Stories3 months ago
Top Stories3 months agoUrgent Farewell: Joleen Chaney Leaves Legacy at KFOR
-

 Top Stories3 months ago
Top Stories3 months agoMarc Buoniconti’s Legacy: 40 Years Later, Lives Transformed
-

 Lifestyle4 months ago
Lifestyle4 months agoKelsea Ballerini Launches ‘Burn the Baggage’ Candle with Ranger Station
-

 Top Stories3 months ago
Top Stories3 months agoCarson Wentz Out for Season After Shoulder Surgery: Urgent Update