Science
Researchers Enhance Energy Efficiency with Innovative Heat Engine
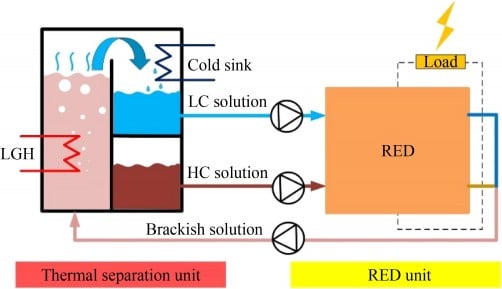
Researchers at Taiyuan University of Technology in China have developed a new reverse electrodialysis heat engine (REDHE) that integrates helium-gap diffusion distillation (HGDD). This innovative technology aims to enhance energy efficiency by converting wasted low-grade heat (LGH) into electricity, addressing the critical issue of energy resource depletion. The findings were published in the journal Frontiers in Energy.
The study details how the REDHE operates effectively at normal atmospheric pressure, making it suitable for the reverse electrodialysis process. By optimizing key parameters such as molality of the cold stream, inlet temperatures, and the dimensions of helium gaps and stream channels, the researchers achieved a maximum energy conversion efficiency of 2.96%. This milestone was reached by reducing the helium gap thickness to 3 mm and extending the stream channels to 5 meters.
Methodology and Implications
Utilizing a validated mathematical model, the research team analyzed the impacts of various parameters on the performance of the REDHE. The study underscores HGDD’s role as a thermal separation unit, which significantly boosts the efficiency of the REDHE technology. The results indicate that advancements in this area could help alleviate energy shortages and contribute to reductions in carbon emissions.
This research, led by Junyong Hu and his colleagues, aligns with the goals of cleaner and more intelligent energy control, particularly in coal and electricity sectors. The project received support from the Fundamental Research Program of Shanxi Province and the China Postdoctoral Science Foundation.
The potential applications of this technology extend beyond mere energy generation. By harnessing low-grade heat, industries could significantly reduce their environmental impact, paving the way for more sustainable practices. The findings present a promising step forward in the quest for efficient energy solutions that meet global demands while minimizing ecological footprints.
For further details, the original study can be accessed through the link: https://link.springer.com/article/10.1007/s11708-024-0947-3 and https://journal.hep.com.cn/fie/EN/1159579891962273821.
-

 Science4 weeks ago
Science4 weeks agoUniversity of Hawaiʻi Joins $25.6M AI Project to Monitor Disasters
-

 Business1 month ago
Business1 month agoForeign Inflows into Japan Stocks Surge to ¥1.34 Trillion
-

 Top Stories1 month ago
Top Stories1 month agoBOYNEXTDOOR’s Jaehyun Faces Backlash Amid BTS-TWICE Controversy
-

 Top Stories1 month ago
Top Stories1 month agoCarson Wentz Out for Season After Shoulder Surgery: Urgent Update
-

 Top Stories1 month ago
Top Stories1 month agoMarc Buoniconti’s Legacy: 40 Years Later, Lives Transformed
-

 Health1 month ago
Health1 month agoInnovative Surgery Restores Confidence for Breast Cancer Patients
-

 Lifestyle2 months ago
Lifestyle2 months agoKelsea Ballerini Launches ‘Burn the Baggage’ Candle with Ranger Station
-

 Sports2 months ago
Sports2 months agoSteve Kerr Supports Jonathan Kuminga After Ejection in Preseason Game
-

 Science2 months ago
Science2 months agoChicago’s Viral ‘Rat Hole’ Likely Created by Squirrel, Study Reveals
-

 Lifestyle2 months ago
Lifestyle2 months agoDua Lipa Celebrates Passing GCSE Spanish During World Tour
-

 Entertainment2 months ago
Entertainment2 months agoZoe Saldana Advocates for James Cameron’s Avatar Documentary
-

 Politics2 months ago
Politics2 months agoDallin H. Oaks Assumes Leadership of Latter-day Saints Church








