Science
T. rex Growth Study Reveals New Insights into Age and Maturity
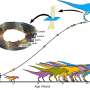
Paleontologists have uncovered new insights into the growth patterns of the Tyrannosaurus rex, revealing that this iconic dinosaur continued to grow until the age of 40. This finding challenges previous estimates that suggested T. rex ceased growing by age 25. The research, conducted by a team led by scientists from the University of California, Berkeley, utilized a method of counting annual growth rings in fossilized leg bones, similar to how one would determine the age of a tree.
The study, published in 2023, analyzed the growth rings in the femurs of several T. rex specimens. Researchers found that these growth rings, which can indicate the age of the dinosaur at various stages of its life, revealed a slower growth rate than previously thought. This slower growth trajectory indicates that T. rex took significantly longer to reach its full size, potentially impacting its ecological role as a top predator.
As the largest known terrestrial carnivore, T. rex has long fascinated both scientists and the public. The findings suggest that, unlike many modern reptiles that grow continuously throughout their lives, T. rex had a more prolonged maturation process. This could have implications for understanding the life history and ecology of this formidable predator.
In the past, estimates based on growth rings indicated that T. rex typically reached maturity by age 25, with most growth occurring in the first two decades of life. The new research indicates that these dinosaurs not only grew larger than previously believed but also continued to develop for an additional 15 years. The implications of this extended growth period are significant, as it may influence how scientists view the survival strategies of T. rex during its time on Earth.
The researchers employed advanced imaging techniques to analyze the bone structure and growth patterns of these fossils. By examining the histological characteristics of the bones, they were able to determine the rate of growth and the age at which T. rex individuals reached certain sizes. The study provides a more complete picture of the life cycle of these iconic dinosaurs.
This groundbreaking research opens new avenues for understanding the biology of T. rex and its contemporaries. The findings may inspire further studies into the growth patterns of other dinosaur species, shedding light on the evolutionary adaptations that allowed these creatures to thrive during the Late Cretaceous period.
The implications of this study extend beyond paleontology. Understanding the growth patterns of T. rex could provide insights into the ecological dynamics of prehistoric ecosystems, influencing how current ecosystems are studied and managed. As researchers continue to uncover details about the lives of dinosaurs, the legacy of T. rex remains a vital part of our understanding of Earth’s ancient past.
-

 Science3 months ago
Science3 months agoUniversity of Hawaiʻi Joins $25.6M AI Project to Monitor Disasters
-

 Business3 months ago
Business3 months agoForeign Inflows into Japan Stocks Surge to ¥1.34 Trillion
-

 Entertainment2 months ago
Entertainment2 months agoHudson Williams Gains Popularity as Breakout Star on Heated Rivalry
-

 World3 months ago
World3 months agoBoeing’s Merger with McDonnell Douglas: A Strategic Move Explained
-

 Science2 months ago
Science2 months ago$1.25M Grant Advances Hawaiʻi’s Real-Time Hazard Monitoring
-

 Entertainment3 months ago
Entertainment3 months agoSydney Sweeney Embraces Body Positivity Amid Hollywood Challenges
-

 Top Stories3 months ago
Top Stories3 months agoBOYNEXTDOOR’s Jaehyun Faces Backlash Amid BTS-TWICE Controversy
-

 Top Stories3 months ago
Top Stories3 months agoUrgent Farewell: Joleen Chaney Leaves Legacy at KFOR
-

 World3 months ago
World3 months agoFrench Film Explores Group Therapy in ‘Group – The Schopenhauer Project’
-

 Top Stories3 months ago
Top Stories3 months agoMarc Buoniconti’s Legacy: 40 Years Later, Lives Transformed
-

 Lifestyle4 months ago
Lifestyle4 months agoKelsea Ballerini Launches ‘Burn the Baggage’ Candle with Ranger Station
-

 Top Stories3 months ago
Top Stories3 months agoCarson Wentz Out for Season After Shoulder Surgery: Urgent Update









